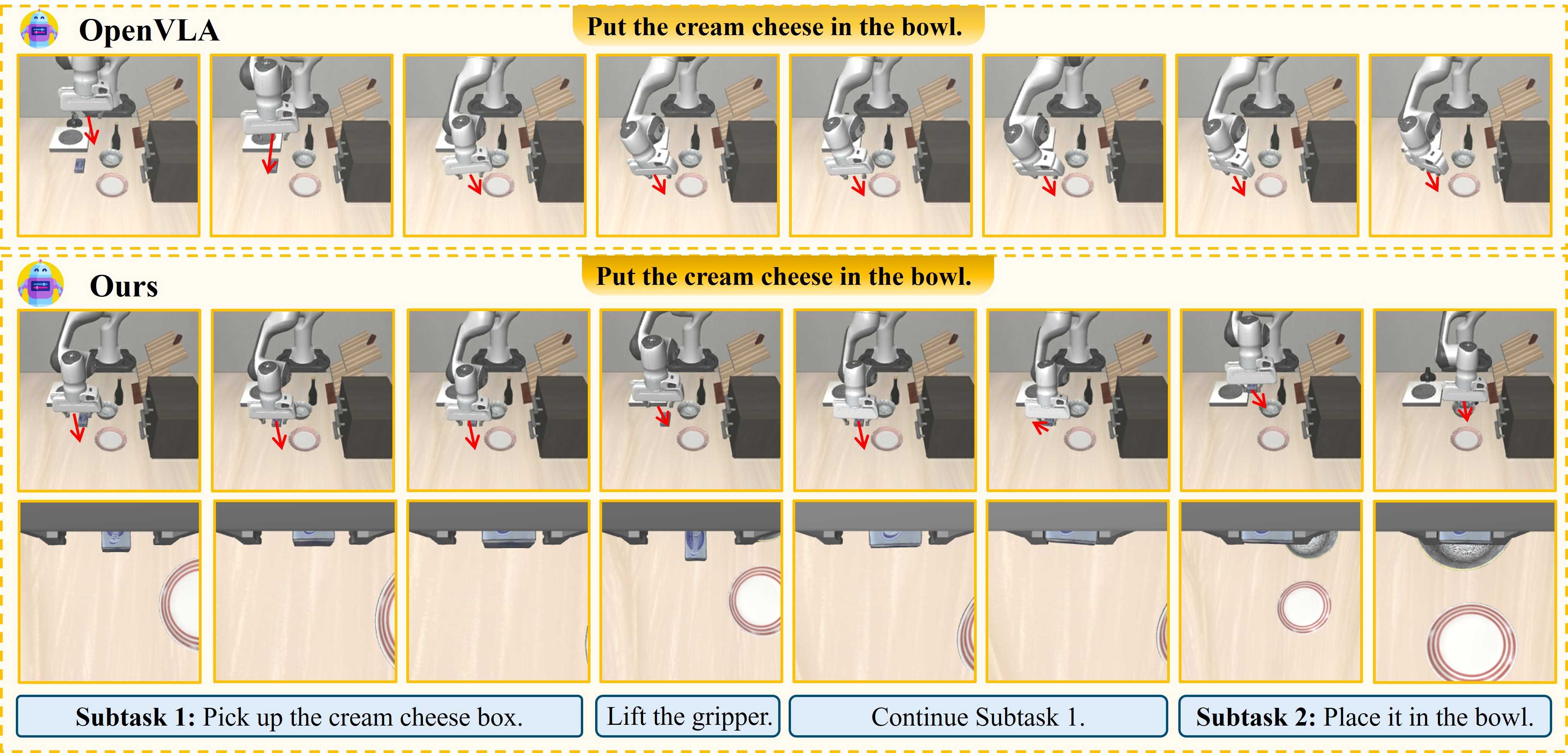
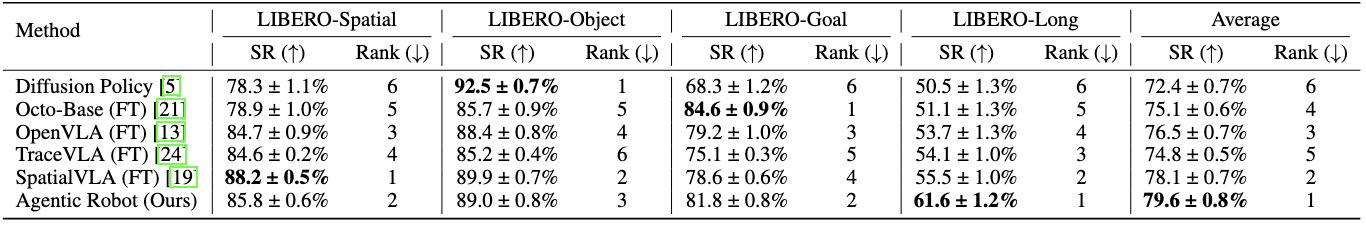
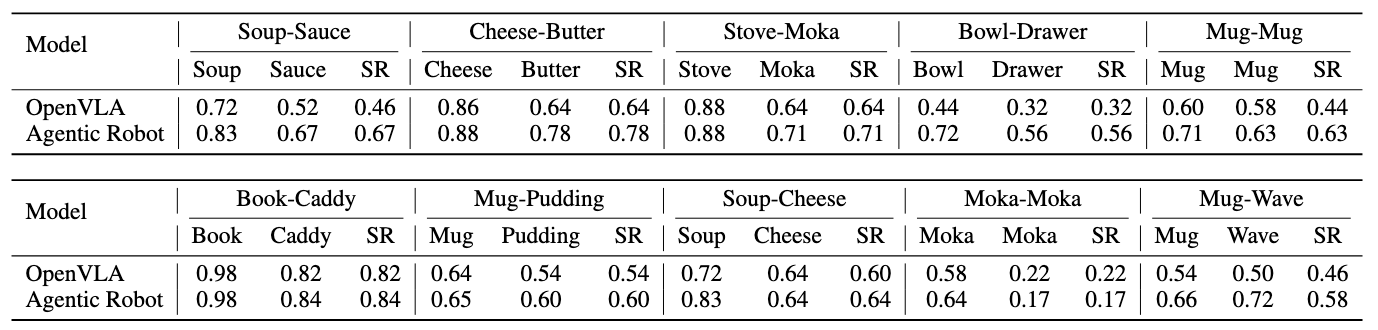
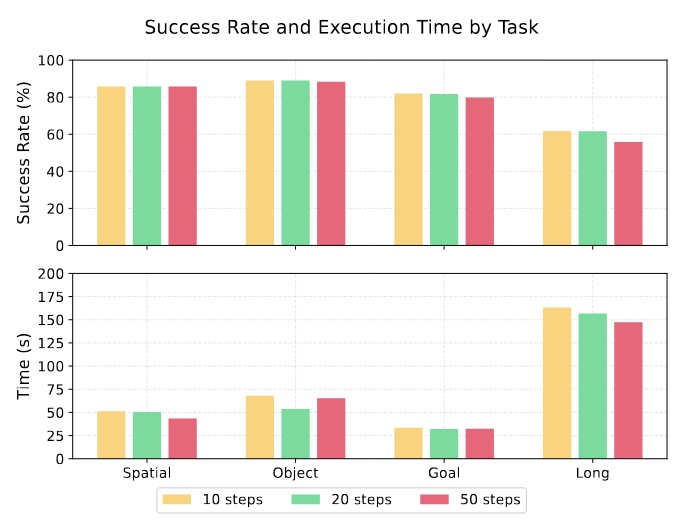
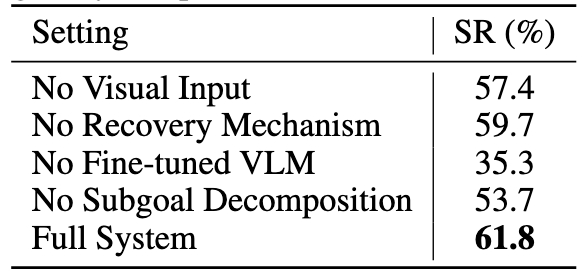
Long-horizon robotic manipulation poses significant challenges for autonomous systems, requiring extended reasoning, precise execution, and robust error recovery across complex sequential tasks. Current approaches, whether based on static planning or end-to-end visuomotor policies, suffer from error accumulation and lack effective verification mechanisms during execution, limiting their reliability in real-world scenarios. We present Agentic Robot, a brain-inspired framework that addresses these limitations through Standardized Action Procedures (SAP)—a novel coordination protocol governing component interactions throughout manipulation tasks. Drawing inspiration from Standardized Operating Procedures (SOPs) in human organizations, SAP establishes structured workflows for planning, execution, and verification phases. Our architecture comprises three specialized components: (1) a large reasoning model that decomposes high-level instructions into semantically coherent subgoals, (2) a vision-language-action executor that generates continuous control commands from real-time visual inputs, and (3) a temporal verifier that enables autonomous progression and error recovery through introspective assessment. This SAP-driven closed-loop design supports dynamic self-verification without external supervision. On the LIBERO benchmark, Agentic Robot achieves state-of-the-art performance with an average success rate of 79.6%, outperforming SpatialVLA by 6.1% and OpenVLA by 7.4% on long-horizon tasks. These results demonstrate that SAP-driven coordination between specialized components enhances both performance and interpretability in sequential manipulation, suggesting significant potential for reliable autonomous systems.